Genetic modification is a method that has been carried out indirectly for thousands of years through the controlled or selective reproduction of plants and animals.
Today it is easier with the help of modern biotechnology, thanks to which it is faster to target a specific gene for more precise alteration of the organism through genetic engineering.
What is genetic modification?
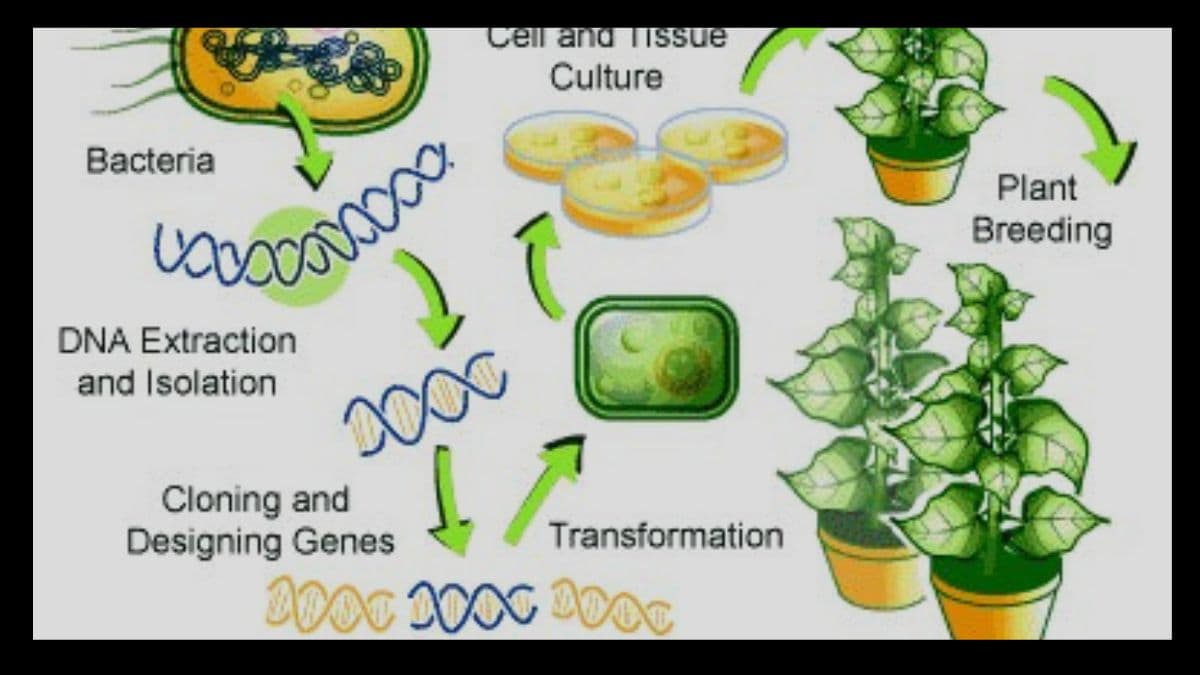
- Genetic modification technology consists of inserting DNA into the genome of an organism in order to produce a genetically modified plant.
- The new DNA is transferred to plant cells, after which the cells are grown in tissue cultures where they develop into plants.
- The seeds produced by these plants will have the new DNA.
- The genetic composition of all living organisms determines their characteristics. It also depends on the interaction with its environment.
- The genetic makeup of an organism is known as genome in which all plants and animals are made of DNA.
- The genome encompasses genes, regions of DNA that carry the instructions for making proteins that give the plant its characteristics.
- For example, the color of flowers is decided by genes that contain the template to create proteins involved in the production of the pigments that color the petals.
The genetic modification process:
For the genetic modification procedure to be carried out in plants it involves adding a specific stretch of DNA to the plant’s genome. This gives it new or varied characteristics.
This could include altering the way the plant grows or protecting it from a particular disease.
The fresh DNA becomes part of the genome of the transgenic plant that would be encapsulated in the seeds produced by these plants.
The first step in producing a transgenic plant requires the transition of DNA into a plant cell.
- One of the methods used to transmit DNA is to cover the surface of small metal particles with the corresponding DNA fragment and flood plant cells with the components.
- The second method is to use a bacteria or a virus. There are many viruses and bacteria that transmit their DNA to a host cell as a natural part of their life cycle.
- For transgenic plants, the most commonly used bacteria is called Agrobacterium tumefaciens.
- The chosen gene is transferred to the bacteria and the bacterial cells then transport the new DNA to the genome of the plant cells.
- Plant cells that have successfully adopted the DNA are grown to create a new plant later.
- This could only be possible thanks to individual plant cells that have a remarkable capacity to produce entire plants.
- On some occasions, the DNA transfer procedure can occur without intentional human intervention.
There are other ways to change crop genomes, some of which are:
1.Modification of traditional crops
The first type is the traditional plant modification technique, such as selective breeding and crossing, which has existed for almost 10,000 years. Most of the foods we consume today were initially developed using a combination of traditional methods.
2. Genetic engineering
The second is genetic engineering, which is a method that, among other things, allows scientists to duplicate a gene with a desired characteristic in one organism and introduce it into another.
Genetic engineering has been used since the 1970s and shapes the scientific advances we have made in the study of DNA.
3. Genome editing
Genome editing is a modern method that provides scientists with more precise and specific paths to develop new crop varieties. Genome editing tools can make it more efficient and faster to formulate modifications that were previously done through traditional breeding.
Categories: Optical Illusion
Source: ptivs2.edu.vn