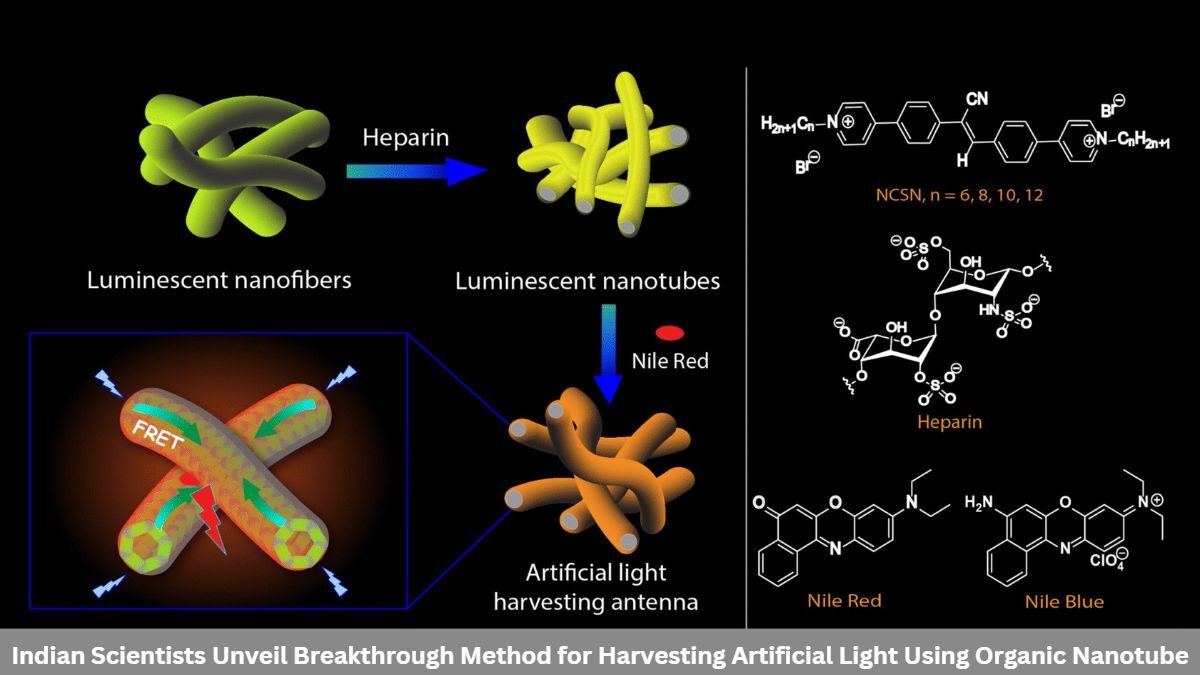
A group of Indian scientists has made a groundbreaking discovery in the field of artificial light harvesting. Inspired by the natural process of photosynthesis, researchers from the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER), Kolkata and SN Bose National Center for Basic Sciences (SNBNCBS), Kolkata, developed a novel method using a fluorescent organic molecule and a therapeutically important component. biopolymer.
These organic nanotubes have a variety of potential applications, including solar cells, photocatalysis, optical sensors, and tunable multicolor light-emitting materials. Similar to how plants use chlorophyll to convert sunlight into energy, scientists used the organic nanotube to absorb artificial light and transfer the energy to a dye molecule such as Nile Red and Nile Blue. dye molecule emits a color tone from initial greenish-yellow to orange-red, including white light.
Compared to traditional methods, this new approach is more efficient at capturing artificial light and has the added benefit of producing a wider range of colors. Researchers believe this breakthrough could pave the way for the development of advanced solar cells, optical sensors and light-emitting devices.
The study detailing this innovative method was published in the prestigious journal Nature Communications. This publication highlights the importance and potential impact of research conducted by Indian scientists.
What are organic nanotubes?
Organic nanotubes are tubular structures formed by organic molecules such as carbon and hydrogen. They have a diameter of a few nanometers and can be several micrometers long. These nanotubes are capable of absorbing light and converting it into electrical energy, a process known as photovoltaics.

Organic nanotubes have unique properties that make them attractive for use in various applications, including electronics, energy harvesting, and biomedical devices. They can be synthesized using a variety of techniques, including chemical vapor deposition, self-assembly, and electrochemical methods. The development of organic nanotubes has opened new possibilities for generating electricity in a sustainable and environmentally friendly way.
Applications of artificial light harvesting:
The new method is promising for several practical applications:
- Solar cells: By collecting artificial light, more efficient solar cells can be designed, capable of converting a greater percentage of sunlight into electricity.
- Optical sensors: This method opens the possibility of creating innovative optical sensors that can detect different types of light with greater precision.
- Light-emitting devices: The new method allows the development of novel light-emitting devices that can produce a broader spectrum of colors, offering greater flexibility and customization.
The phenomenon observed in this research is called “Förster resonance energy transfer” (FRET) and plays a crucial role in various applications, such as DNA/RNA structure analysis, biological membrane mapping, and performance testing. Real-time PCR.
While still in the early stages of development, this advancement has the potential to revolutionize the utilization and harvesting of artificial light. Indian researchers Dr. Supratim Banerjee and Dr. Suman Chakrabarty envision a future in which this method will transform the way we harness and use artificial light.
Categories: Optical Illusion
Source: ptivs2.edu.vn